To provide observations and information on the emerging fields of landscape scale conservation, heritage preservation, and sustainable community development.
Newsletter
Stay up-to-date with the latest nature, culture and community news.
We won’t spam you or share your information. Newsletters are sent approximately 10 times a year. Unsubscribe at any time.

Parks Stewardship Forum Features Living Landscapes
The most recent edition of the Parks Stewardship Forum (PSF), entitled “Politics, Practice, and the Management of Living Landscapes,” was guest-edited by Brenda Barrett and Eleanor Mahoney from the Living Landscape Observer. This issue examines the conservation of living landscapes at sites worldwide.
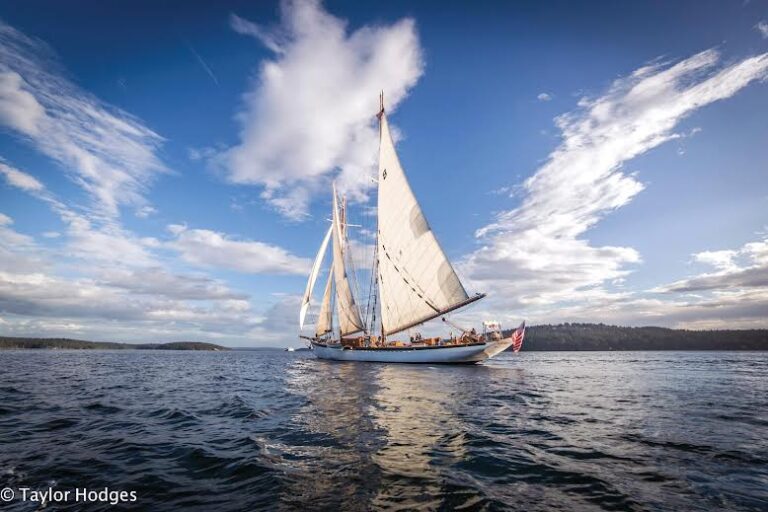

Launching the Maritime Washington National Heritage Area
Watching the development of a national heritage area is a bit like observing the formation of a solar system. Partners large and small are attracted to the heritage area idea like planets around a sun and if the perceived benefits are powerful enough the gravitational force will bind them together around a unified vision. With the conservation movement’s interest in how to build effective large landscape networks examining how this actually happens on the ground might be productive. What lessons can we learn from the formation of the Washington Maritime National Heritage Area?

Looking Back on Landscape Scale Conservation
The origin story of the landscape scale conservation movement has yet to be told. However, in the United States, there has been a long tradition of managing fish and wildlife habitat with the understanding that species preservation required the conservation of wider ecosystems. Today the movement has received reinforcement from the nonprofit sector organizations such as the Network for Landscape Conservation.
Outsized Threats to Large Landscapes
It should come as no surprise to readers of the Living Landscape Observer that conserving large landscapes in the current political climate is no easy task. There are threats to our public lands and proposals to defund the federal programs that conserve our cultural and natural resources. However, the bigger issue is the underlying erosion of landscape scale work throughout our national government. There are systemics challenges to all these efforts that need to be better understood.

Network for Landscape Conservation: A Lesson in Nature and Culture
The Coordinating Committee of the Network for Landscape Conservation gathered for a picture on Boneyard Beach, Bull Island in the Cape Romaine National Wildlife Reserve in South Carolina. The field trip kicked off an April retreat in Charleston South Carolina to finalize the outcomes of the recent National Forum for Landscape Conservationand to identify strategic initiatives to advance the conservation at a landscape scale.The low country region is a great example of a conserved natural landscape with four Federal Wildlife Refuges, designation as the Carolinian-South Atlantic Biosphere Reserve, and ACE Basin Project that manages over 100,000 of protected lands and estuaries. However, it is the cultural heritage of the region, it is one of the centers of Gullah Geechee culture, that makes the landscape of truly global cultural and natural significance.

Parks Stewardship Forum Features Living Landscapes
The most recent edition of the Parks Stewardship Forum (PSF), entitled “Politics, Practice, and the Management of Living Landscapes,” was guest-edited by Brenda Barrett and Eleanor Mahoney from the Living Landscape Observer. This issue examines the conservation of living landscapes at sites worldwide.

Launching the Maritime Washington National Heritage Area
Watching the development of a national heritage area is a bit like observing the formation of a solar system. Partners large and small are attracted to the heritage area idea like planets around a sun and if the perceived benefits are powerful enough the gravitational force will bind them together around a unified vision. With the conservation movement’s interest in how to build effective large landscape networks examining how this actually happens on the ground might be productive. What lessons can we learn from the formation of the Washington Maritime National Heritage Area?

Looking Back on Landscape Scale Conservation
The origin story of the landscape scale conservation movement has yet to be told. However, in the United States, there has been a long tradition of managing fish and wildlife habitat with the understanding that species preservation required the conservation of wider ecosystems. Today the movement has received reinforcement from the nonprofit sector organizations such as the Network for Landscape Conservation.

Outsized Threats to Large Landscapes
It should come as no surprise to readers of the Living Landscape Observer that conserving large landscapes in the current political climate is no easy task. There are threats to our public lands and proposals to defund the federal programs that conserve our cultural and natural resources. However, the bigger issue is the underlying erosion of landscape scale work throughout our national government. There are systemics challenges to all these efforts that need to be better understood.

Network for Landscape Conservation: A Lesson in Nature and Culture
The Coordinating Committee of the Network for Landscape Conservation gathered for a picture on Boneyard Beach, Bull Island in the Cape Romaine National Wildlife Reserve in South Carolina. The field trip kicked off an April retreat in Charleston South Carolina to finalize the outcomes of the recent National Forum for Landscape Conservationand to identify strategic initiatives to advance the conservation at a landscape scale.The low country region is a great example of a conserved natural landscape with four Federal Wildlife Refuges, designation as the Carolinian-South Atlantic Biosphere Reserve, and ACE Basin Project that manages over 100,000 of protected lands and estuaries. However, it is the cultural heritage of the region, it is one of the centers of Gullah Geechee culture, that makes the landscape of truly global cultural and natural significance.


